Request a price list
Available in stock
Leave a request
Due to metabolic reactions, fertilizer potassium is absorbed by soil colloids, which reduces its mobility in the soil, but at the same time, it remains available for plant nutrition. Chlorine ions remain in the soil solution, so they are easily washed out of the arable soil layer. Therefore, their effect on plants is sometimes exaggerated. Fertilizer acidifies the soil solution only with long-term use in large doses. To reduce the negative effects of chlorine, chlorine-containing potash fertilizers should be applied in the fall in optimal doses during the main tillage. Under the influence of atmospheric precipitation, chlorine ions are washed out of the root layer of the soil, and potassium ions remain at the place of fertilizer application. Usually, on soils of medium and heavy loamy granulometric composition, fertilizer potassium does not move from the meter-long, i.e. root-bearing soil layer.
The experience of world agriculture has shown that potassium is an element of high yield. First of all, potash fertilizers are needed in the sod-podzolic soils of Polesie and podzolic soils of forest-steppe. The soils of the southern forest-steppe and almost all soils of the steppe are characterized by an increased and high content of mobile potassium compounds. Potash fertilizers are most effective on light sod-podzolic soils, drained peatlands, Gray forest soils, and chernozems of leached forest-steppe.
Due to the antagonism of potassium and calcium, there is a need to increase the doses of mineral fertilizers during liming and on soils with a reaction close to neutral. Simultaneously with the improvement of the potash regime of the soil, the efficiency of liming also increases.
With the systematic cultivation of potash crops and the application of high doses of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers, the efficiency of potash fertilizers increases. This is explained by the depletion of unfertilized soils for potassium due to its removal by crops. Potassium, unlike phosphorus, can be added in reserve only for 2-3 years.
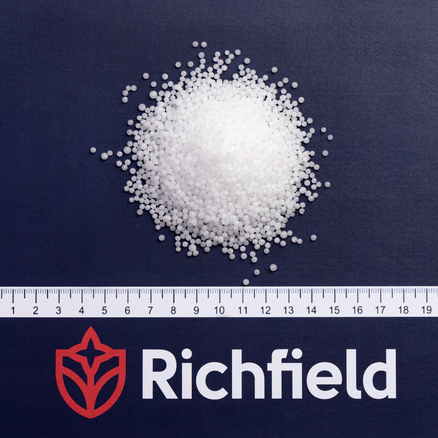
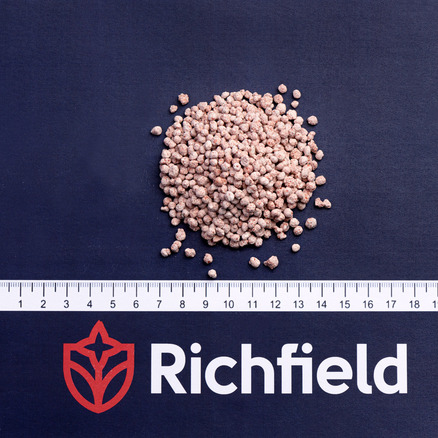
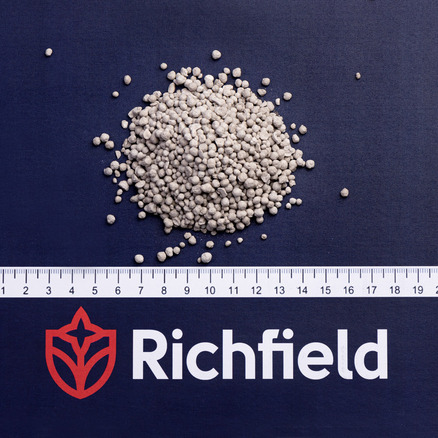
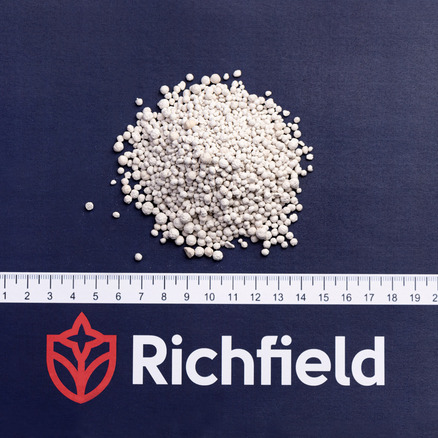
- Potassium chloride belongs to simple fertilizers;
- it does not lose its physical properties during storage;
- the statistical solidity of pellets is not less than 5 MPa 100% friability;
- it is highly soluble in soil solution and interacts with the soil absorbent complex;
- it interacts well with the soil absorption complex;
- it quickly compensates for potassium deficiency;
- it partially covers a shortage of sulfur;
- when applied in rows it does not limit the germination of seeds of grain crops;
- the aftereffect of phosphorus is well manifested on subsequent crops.
- The average dose of potash fertilizers for most crops is 45-60 kg/ha of K2O. For crops that take a lot of potassium with the crop (beets, potatoes, tobacco, sunflower, fruit, and some vegetables), fertilizer doses must be increased to 90-120 kg/ha K2O. The natural effect of potash fertilizers is manifested when the content of mobile potassium compounds is 60-100 mg/kg.
- Usually, the dose of potash fertilizers in intensive farming conditions should correspond to the withdrawal of potassium from the field by agricultural products (basic and non-commodity) with a value of the content of exchange potassium in the soil close to optimal. This can be seen in the example of developed European countries, where on fertile soils the doses of potash fertilizers are supportive and almost do not change.
Move to the catalog
Leave your contact details
and our manager will contact you soon to clarify the details of the order